
Vandetanib; 443913-73-3; Zactima; ZD6474; Caprelsa; ZD 6474; ch 331, azd 6474
cas 338992-00-0 free form
338992-48-6 HCl
338992-53-3 monotrifluoroacetate
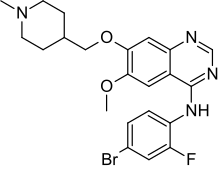
N-(4-Bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-(1-methylpiperidin-4-ylmethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine
Vandetanib (INN, trade name Caprelsa) is an anti-cancer drug that is used for the treatment of certain tumours of the thyroid gland. It acts as a kinase inhibitor of a number of cell receptors, mainly the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), theepidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and the RET-tyrosine kinase.[1][2] The drug was developed by AstraZeneca.
Orphan drug designation has been assigned in the E.U. for the treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma. In 2005, orphan drug designation was also assigned in the U.S. for several indications, including treatment of patients with follicular thyroid carcinoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma, anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, and locally advanced and metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma. In 2013, orphan drug designation has been assigned in Japan as well for the treatment of thyroid cancer.
Approvals and indications
Vandetanib was the first drug to be approved by FDA (April 2011) for treatment of late-stage (metastatic) medullary thyroid cancer in adult patients who are ineligible for surgery.[3] Vandetanib was first initially marketed without a trade name,[4] and is being marketed under the trade name Caprelsa since August 2011.[5]
Vandetanib is an orally active vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2/KDR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, originally developed by AstraZeneca, which was filed for approval in the U.S. and the E.U. for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in combination with chemotherapy, in patients previously treated with one prior anticancer therapy.
However, in late 2009 the company withdrew both the U.S and the EU applications. In 2010, AstraZeneca discontinued development of this compound for the treatment of NSCLC. In 2011, the FDA approved vandetanib for the treatment of medullary thyroid cancer. Also in 2011, a positive opinion was assigned to the regulatory application filed in the E.U. for this indication and in Japan was filed for approval.
Final EMA approval was granted in February 2012 and first E.U. launch took place in the U.K. in 2012.
2011 年 4 月 6 by the FDA-approved surgical resection can not be used for locally advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer (medullary thyroid cancer, MTC) of the drug. Vandetanib is vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor, VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR) antagonists, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (tyrosine kinase inhibitor). Produced by AstraZeneca.
The synthetic route is as follows:
………………
………………………..
……….
Design and structure-activity relationship of a new class of potent VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
J Med Chem 1999, 42(26): 5369
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jm990345w
………………………
Radiosynthesis of [(11)C]Vandetanib and [(11)C]chloro-Vandetanib as new potential PET agents for imaging of VEGFR in cancer
Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011, 21(11): 3222
Novel 4-anilinoquinazolines with C-7 basic side chains: Design and structure activity relationship of a series of potent, orally active, VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors
J Med Chem 2002, 45(6): 1300
A novel approach to quinazolin-4(3H)-one via quinazoline oxidation: An improved synthesis of 4-anilinoquinazolines
Tetrahedron 2010, 66(4): 962
………………………………
CN 104098544
http://www.google.com/patents/CN104098544A?cl=en
Vandetanib is a synthetic Anilinoquinazoline, advanced medullary thyroid cancer can not be used for the treatment of surgical treatment (medullary thyroid cancer), chemical name: 4- (4-bromo-2- fluoroanilino) _6_ methoxy -7 – [(l- methylpiperidin-4-yl) methoxy] quinazoline, having the following structural formula I:
[0004] The present method of synthesizing the compound are as follows:
[0005] US Patent US7173038 AstraZeneca announced the following methods:
[0006] Method One:
[0007]
Method two:
A structure in which the synthesis of compounds of formula as follows:
the process is cumbersome, long synthetic route, therefore a need to provide a new synthetic way to overcome these problems.
An aspect provides a compound having the structure of formula II:
Another aspect provides a process for preparing a compound of the structural formula II, a compound of formula III with a compound of formula IV in the presence of a base to give a compound of the structural formula II,
where Μ for methylphenylsulfonyl, methylsulfonyl.
Example: 4- (4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino) -6_ methoxy-7 – [(1-formyl-4-yl) methoxy] quinazoline preparation
[0026] in 50mL two-neck flask was added 4- (4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino) -6-methoxy-7-hydroxy-quinazoline (3. 64g, 0 · Olmol), 1- formyl- 4-p methylsulfonyloxy- methylpiperazine steep (3. 56g, 0 · 012mol) and potassium carbonate (4. 14g, 0.03mol), yellow turbid solution was stirred and heated to 100 ° C, TLC detection to feed completion of the reaction. Down to room temperature, the reaction mixture was slowly poured into l〇〇mL water, stirred, filtered, then the filter cake was washed with 50mL water, 15mL of ethyl acetate and then slurried, filtered and dried to give a pale green solid 4- (4- bromo-2-fluoroanilino) -6-methoxy -7 – [(l- carboxylic acid piperidin-4-yl) methoxy] quinazoline 3. 9g, 80% yield.
[0027] ^ NMR (400Mz, DMS0): δ = 1 1〇-1 29 (m, 2H), δ = 1 40-1 43 (m, 2H), δ = 2 15 (s,….. 1H), δ = 2. 64-2. 73 (m, 1H), δ = 3. 06-3. 12 (m, 1H), δ = 3. 71-3. 74 (d, 1H), δ = 3. 95 (s, 3H), δ = 4 • 03-4. 05 (d, 2H), δ = 4. 20-4. 23 (d, 1H), δ = 7. 20 (s, 1H), δ = 7. 46-7. 48 (m, 1H), δ = 7. 51-7 • 53 (m, 1H), δ = 7. 65-7. 67 (d, 1H), δ = 7. 80 (s, 1H), δ = 8. 01 (s, 1H), δ = 8. 35 (s, 1H), δ = 9. 54 (s, 1H).
[0028] Example 2: Preparation of 4- (4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino) -6-methoxy-7 – [(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl) methoxy] quinazoline preparation
[0029] 4- (4-bromo-2-fluoroanilino) in 100mL three-necked flask, 6-methoxy-7 – [(1-formyl-4-yl) methoxy] quinoline oxazoline (0 · 98g, 2. Ommol), zinc (0 · 6g, 4. 4mmol) and tetrahydrofuran (20mL), stirred pale yellow turbid liquid. At room temperature was added portionwise sodium borohydride (0. 15g, 4. OmmoL), little change in the temperature. Heating
……………………………….
CN 104211649
http://www.google.com/patents/CN104211649A?cl=en
Pharmacokinetics
Vandetanib is well absorbed from the gut, reaches peak blood plasma concentrations 4 to 10 hours after application, and has a half-life of 120 hours days on average, per Phase I pharmacokinetic studies. It has to be taken for about three months to achieve a steady-state concentration. In the blood, it is almost completely (90–96%) bound to plasma proteins such as albumin. It is metabolised to N-desmethylvandetanib via CYP3A4 and to vandetanib-N-oxide via FMO1 and 3. Both of these are active metabolites. Vandetanib is excreted via the faeces (44%) and the urine (25%) in form of the unchanged drug and the metabolites.[2][9][10]
Metabolites of vandetanib (top left): N-desmethylvandetanib (bottom left, via CYP3A4), vandetanib-N-oxide (bottom right, via FMO1 andFMO3), both pharmacologically active, and a minor amount of aglucuronide.[10]
Clinical trials
Non-small cell lung cancer
The drug underwent clinical trials as a potential targeted treatment for non-small-cell lung cancer. There have been some promising results from a phase III trial withdocetaxel.[11] There have also been ambivalent results when used with pemetrexed.[12] Another trial with docetaxel was recruiting in July 2009.[13]
AstraZeneca withdrew EU regulatory submissions for vandetanib (under the proposed trade name Zactima) in October 2009 after trials showed no benefit when the drug was administered alongside chemotherapy.[14]
References
- “Definition of vandetanib”. NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute.
- “Vandetanib Monograph”. Drugs.com. Retrieved 29 August 2012.
- “FDA approves new treatment for rare form of thyroid cancer”. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- “FDA approves orphan drug vandetanib for advanced medullary thyroid cancer” (Press release). AstraZeneca. Retrieved 2011-08-17.
- “AstraZeneca announces trade name CAPRELSA® for vandetanib” (Press release). AstraZeneca. Retrieved 2011-08-17.
- Khurana V, Minocha M, Pal D, Mitra AK (March 2014). “Role of OATP-1B1 and/or OATP-1B3 in hepatic disposition of tyrosine kinase inhibitors.”. Drug Metabol Drug Interact.0 (0): 1–11. doi:10.1515/dmdi-2013-0062. PMID 24643910.
- Haberfeld, H, ed. (2012). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- Khurana V, Minocha M, Pal D, Mitra AK (May 2014). “Inhibition of OATP-1B1 and OATP-1B3 by tyrosine kinase inhibitors.”. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 0 (0): 1–11.doi:10.1515/dmdi-2014-0014. PMID 24807167.
- Martin, P.; Oliver, S.; Kennedy, S. J.; Partridge, E.; Hutchison, M.; Clarke, D.; Giles, P. (2012). “Pharmacokinetics of Vandetanib: Three Phase I Studies in Healthy Subjects”.Clinical Therapeutics 34 (1): 221–237. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.11.011.PMID 22206795.
- “Clinical Pharmacology Review: Vandetanib” (PDF). US Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. 20 August 2010. Retrieved29 August 2012.
- “Vandetanib Shows Clinical Benefit When Combined With Docetaxel For Lung Cancer”. ScienceDaily. 3 June 2009.
- “IASLC: Vandetanib Fails to Improve NSCLC Outcomes with Pemetrexed”. Medpage today. 5 Aug 2009.
- Clinical trial number NCT00687297 for “Study of Vandetanib Combined With Chemotherapy to Treat Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer” at ClinicalTrials.gov
- “Zactima”. European Medicines Agency.
External links
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
N-(4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazolin-4-amine
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Caprelsa |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a611037 |
| Licence data | US FDA:link |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90–96% |
| Metabolism | CYP3A4, FMO1, FMO3 |
| Biological half-life | 120 hours (mean) |
| Excretion | 44% faeces, 25% urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Registry Number | 443913-73-3  |
| ATC code | L01XE12 |
| PubChem | CID: 3081361 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5717 |
| DrugBank | DB08764  |
| ChemSpider | 2338979  |
| UNII | YO460OQ37K  |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:49960  |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL24828  |
| Synonyms | ZD6474 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C22H24BrFN4O2 |
| Molecular mass | 475.354 g/mol |
//////
Filed under: 0rphan drug status, Uncategorized Tagged: ASTRAZENECA, medullary thyroid cancer, Orphan Drug Designation, VANDETANIB









